Research Funding
Genomic Health Incorporated, an Exact Sciences corporation.
Background
Adverse pathology (AP) at radical prostatectomy (RP) is often used as a proxy for long-term prostate cancer outcomes. The goal of this study was to assess the association of AP at RP, defined as high-grade (> Grade Group 3) and/or non-organ confined disease (pT3), with distant metastasis and prostate cancer death.Methods:A stratified cohort sample of 428 patients was used to evaluate the association of adverse pathology with the risk of distant metastases and prostate cancer-specific mortality over 20 years after prostatectomy in 2641 patients treated between 1987-2004. Cox regression of cause-specific hazards was used to estimate the absolute risk of both endpoints, with death from other causes treated as a competing risk. Subgroup analysis in patients with low/intermediate risk disease potentially eligible for active surveillance was performed.
Results
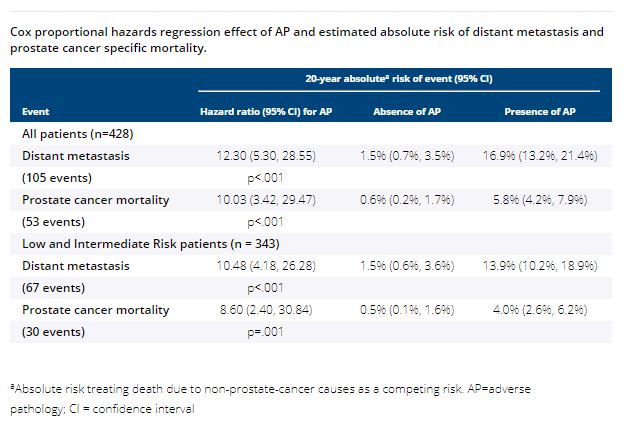
Among the 428 patients, 343 had AUA Low or Intermediate risk disease and 85 had High risk disease. Median follow-up time was 15.5 years (IQR 14.6–16.6 years). Using the cohort sampling weights for estimation, at RP 29.8% of patients had high-grade disease, 42.3 % had non-organ confined disease, 19.3% had both, and thus 52.8% had AP. Adverse pathology was highly associated with metastasis and prostate cancer mortality in the overall cohort (HR 12.30, 95% CI 5.30-28.55, and 10.03, 95% CI 3.42-29.47, respectively, both p<0.001), and in the low/intermediate risk subgroup potentially eligible for active surveillance (HR 10.48, 95% CI 4.18-26.28, and 8.60, 95% CI 2.40-30.84, respectively, both p≤0.001).
Conclusions
Adverse pathology at radical prostatectomy is highly associated with future development of metastasis and prostate cancer mortality and may be used as a short-term predictor of outcomes.