Background
Approximately 20% of mCRPC has alterations in genes associated with HRR and is responsive to PARP inhibitors (PARPi) such as NIRA. Combined PARPi with androgen receptor pathway targeting may also benefit unselected mCRPC. MAGNITUDE assessed whether adding NIRA to AAP improves outcomes in pts with mCRPC with or without alterations in HRR associated genes.
Methods
MAGNITUDE (NCT03748641) is a randomized, double-blind phase 3 study. In eligible mCRPC pts, ≤4 mos of prior AAP for mCRPC was allowed. Pts with (HRR biomarker [BM]+; ATM, BRCA1, BRCA2, BRIP1, CDK12, CHEK2, FANCA, HDAC2, PALB2) and without specified gene alterations (HRR BM-) were randomized 1:1 to receive NIRA 200 mg once daily + AAP or placebo (PBO) + AAP. Primary endpoint was radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS) assessed by blinded independent central review (BICR) in the BRCA1/2 group followed by all HRR BM+ pts. Secondary endpoints were time to initiation of cytotoxic chemotherapy (TTCC), time to symptomatic progression (TTSP) and overall survival (OS). Other endpoints included time to PSA progression (TTPP) and objective response rate (ORR).
Results
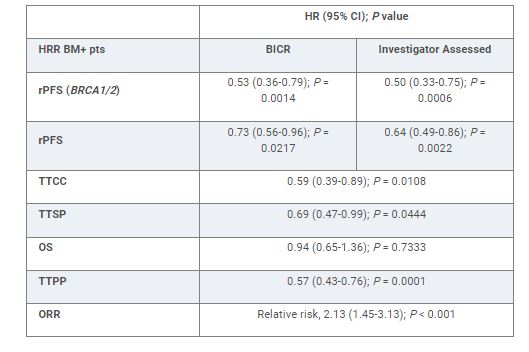
423 HRR BM+ pts were randomized to NIRA + AAP (n = 212) or PBO + AAP (n = 211). Median age was 69, 23% had prior AAP, 21% had visceral metastases, and 53% had BRCA1/2 mutations. Median follow-up was 18.6 mos. NIRA + AAP significantly improved rPFS by BICR in the BRCA1/2 subgroup and in all HRR BM+ pts, reducing the risk of progression or death by 47% (16.6 vs 10.9 mo) and 27% (16.5 vs 13.7 mo) respectively (Table), vs PBO + AAP. Investigator assessed rPFS was consistent with BICR. NIRA + AAP delayed TTCC, TTSP, and TTPP and improved ORR in HRR BM+ pts (Table). First interim analysis of OS is immature. The preplanned futility analysis in 233 HRR BM- pts showed no benefit of adding NIRA to AAP in the prespecified composite endpoint (first of PSA progression or rPFS; HR, 1.09; 95% CI, 0.75-1.57). No new safety signals were seen. In HRR BM+ pts, 67% and 46.4% had grade 3/4 AEs and 9% and 3.8% discontinued treatment in the NIRA + AAP and PBO + AAP arms, respectively. There were no clinically significant differences in overall quality of life (FACT-P).
Conclusions
NIRA + AAP improves rPFS and other clinically relevant outcomes in pts with mCRPC and alterations in HRR associated genes. There was no evidence of benefit with the addition of NIRA to AAP in HRR BM- pts with mCRPC.