Background
At the primary analysis of PROpel (NCT03732820; data cut-off [DCO]: 30/07/21), abi + ola significantly prolonged radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS) vs pbo + abi in 1L mCRPC (HR 0.66, 95% CI 0.54–0.81; P<0.0001). Overall survival (OS) trended towards a benefit with abi + ola vs abi + pbo (28.6% maturity; HR 0.86, 95% CI 0.66–1.12). We report biomarker analysis from the primary analysis and updated overall survival and safety data from a planned OS interim analysis (DCO2).
Methods
PROpel is a double-blind, pbo-controlled trial. 796 pts were randomized 1:1 to ola (300 mg twice daily [bid]) or pbo, and abi (1000 mg once daily) + prednisone or prednisolone (5 mg bid), irrespective of homologous recombination repair gene mutation (HRRm) status. The primary endpoint was rPFS by investigator assessment. OS was a key secondary endpoint. Aggregated results from tumour tissue (FoundationOne®CDx) and circulating tumour DNA (FoundationOne®Liquid CDx) tests were used to classify pts HRRm status.
Results
Pts with HRRm, including BRCAm, were balanced between treatment arms and rPFS favoured abi + ola for all biomarker subgroups, including pts with non-HRRm, HRRm and BRCAm status (HR 0.76, 0.50 and 0.23 respectively; Table). Sensitivity analysis of rPFS by blinded independent central review was consistent. At DCO2 (14/03/22) rPFS was consistent with the primary analysis (25.0 vs 16.4 months; HR 0.67, 95% CI 0.56–0.81). A trend towards improved OS with abi + ola vs abi + pbo continued (maturity 40%; HR 0.83; 95% CI 0.66–1.03). Safety and tolerability results remained stable.
Conclusions
Meaningful rPFS improvement of ≥5 months was observed with abi + ola vs abi + pbo in all assessed biomarker subgroups. Updated results show a continuing trend towards improved OS and support a superior clinical benefit with abi + ola vs abi + pbo as 1L therapy for pts with mCRPC. Table: 1357O
Biomarker subgroup analyses
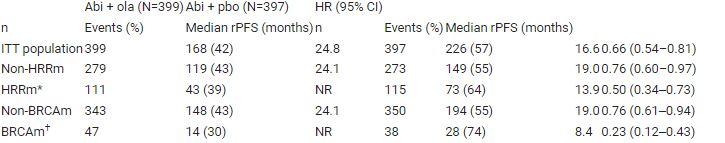
*Genes assessed were ATM, BRCA1, BRCA2, BARD1, BRIP1, CDK12, CHEK1, CHEK2, FANCL, PALB2, RAD51B, RAD51C, RAD51D and RAD54L † BRCA1 and/or BRCA2ITT, intention-to-treat, NR, not reachedHRRm unknown pts (n=18) were excluded from the analysis.
Clinical trial identification
NCT03732820.